
India, a country with a rich history and a diverse cultural heritage, has always embraced the spirit of exploration and innovation. Missions of ISRO has most remarkable embodiments of this indomitable spirit of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
Since its inception in 1969, ISRO has been at the forefront of space exploration, making significant strides in satellite technology, interplanetary missions, and scientific research.
In this blog, we’ll take a journey through the top 7 missions of ISRO that have etched their mark in space history.
TOP 7 MISSIONS OF ISRO
1. Aryabhata (1975)

India’s first satellite was the Aryabhata spacecraft, which was launched on April 19, 1975, by a Soviet Kosmos-3M rocket from Kapustin Yar and was named after the well-known Indian astronomer. It was one of the first missions of ISRO.
Aryabhata’s successful launch was made possible by cooperation between India and the Soviet Union. The Soviet Union pledged to provide technical support and a launch vehicle for the satellite as part of a contract inked in 1972.
The Soviet space program’s workhorse Kosmos-3M rocket was chosen to launch Aryabhata into orbit. On April 19, 1975, the satellite was launched from the Russian launch pad at Kapustin Yar.
This milestone mission laid the foundation for future space endeavors and put India on the global space map.
2. Chandrayaan-1 (2008)

In 2008, an Indian rocket named PSLV carried Chandrayaan-1 into space, and a few days later, it reached the Moon’s orbit. For the next four days, Chandrayaan-1 used its engines smartly to settle into a circular orbit around 62 miles above the Moon’s surface.
This orbit allowed it to observe the Moon closely using its 11 instruments, with half of them provided by NASA and European space agencies. Although, sadly, on August 29, 2009, communication with the orbiter was lost, it had already achieved its primary goal of finding water on the Moon, which was a big deal for ISRO.
The main goal of this mission was to explore the Moon’s surface and check if there is any water. It used special instruments to study the Moon closely. The exciting thing is that it found water ice in the dark craters of the Moon, where sunlight never reaches.
3. Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) – 2013

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) embarked on a historic journey on November 5, 2013, as it launched its very first spacecraft set to explore the enigmatic realm of Mars.
Aptly named Mangalyaan, meaning “Mars craft” in English, this ambitious mission was not only designed to investigate the mysteries of the Red Planet but also to test vital technologies required for future interplanetary expeditions within our solar system.
It marked a significant milestone for ISRO as it stepped into the uncharted territory of Martian exploration.With precision and determination, Mangalyaan traversed the vast expanse of space, venturing toward its distant target.
Finally, on September 23, 2014, the spacecraft achieved a momentous feat by skillfully inserting itself into the orbit of Mars. It is one of the significant missions of ISRO.
4. Chandrayaan-2 (2019)

In the wake of Chandrayaan-1’s triumph, ISRO set its sights even higher and embarked on a groundbreaking mission called Chandrayaan-2, launched on July 22, 2019. This audacious venture had an ambitious objective – to delve into the uncharted territory of the Moon’s south polar region.
To achieve this, the scientists equipped Chandrayaan-2 with a trio of spacecraft – a lander, an orbiter, and a rover – and assigned each a vital role in unraveling lunar mysteries.
The journey of Chandrayaan-2 began with all three vehicles venturing together into lunar orbit in July 2019. The lander, carrying the precious rover, aimed to skillfully touch down in the unexplored southern hemisphere of the Moon.
The orbiter, on the other hand, assumed the responsibility of maintaining an aerial vigil over the lunar surface. Ensuring the continuous flow of invaluable observations and data.Chandrayaan-2 was a testimony to ISRO’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration.
5. ASTROSAT
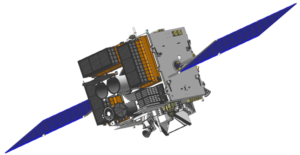
The ISRO‘s Astrosat satellite is on a specific astronomy mission. The goal of the project is to simultaneously observe celestial sources in the X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands. Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, served as the launchpad for the Astrosat satellite.
The Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) or Sriharikota Range (SHAR) is the name of the launch facility. The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) C-30 is the rocket for this launch. They put the satellite into a 650 km orbit. They planned the mission over the course of five years.
6. NAVIC

Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) is a satellite-based navigation system developed by ISRO to cater to India’s positioning, navigation, and timing requirements.
Initially known as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), NavIC’s objective is to provide accurate and reliable navigation services. Catering to both civilian and civil aviation needs.
Despite receiving approval in 2006, NavIC commenced full-scale operations only in 2018. At that time, they deployed a constellation of seven satellites to cover the entire geographical expanse of India.
These satellites include three geostationary and four geosynchronous satellites, strategically positioned in higher orbits to ensure comprehensive coverage.
They initially named the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) NavIC and designed it to provide accurate and reliable navigation services catering to both civilian and civil aviation needs.
7. XPOSAT

The Indian Space Research Organisation in partnership with the Raman Research Institute is building an X-ray polarimeter satellite (XPoSat). To explore the varied dynamics of powerful astronomical X-ray sources under adverse circumstances.
In harsh environments, XPoSat will investigate a variety of behaviors of intense astronomical X-ray sources.
We note that it is the world’s second polarimetry mission and the first in India. With the goal of examining the dynamics of bright astronomical X-ray sources in adverse circumstances. The other important mission launched in 2021 is the NASA Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE).
End Of Space Exploration
ISRO’s top 7 missions showcase the organization’s diverse range of achievements. From lunar and interplanetary exploration to earth observation and communication technologies.
With each successful missions of ISRO, it has consistently demonstrated India’s capability to leverage space technology. That is for the benefit of its citizens and the scientific community worldwide.
As ISRO continues to push boundaries and explore new frontiers, it remains an inspiration for space agencies globally. Solidifying its position as a trailblazer in the field of space exploration.





